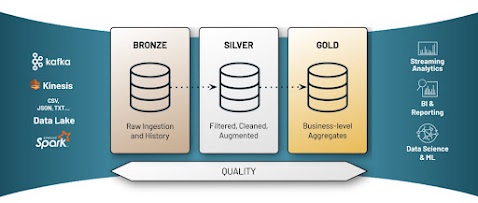
Data warehousing is a crucial aspect of modern business intelligence. The Medallion Architecture is a popular approach for designing data warehouses that can effectively meet the needs of an organization. The Medallion Architecture consists of three layers: Bronze, Silver, and Gold. In this blog post, we'll explore each of these layers and their role in building an effective data warehouse.
Bronze Layer:
The Bronze layer is the first layer of the Medallion Architecture. This layer is responsible for storing raw data. The data is typically loaded into this layer without any transformation or modification. The goal of this layer is to store all the data that an organization collects in its original form, without losing any information. This data can come from various sources, including transactions, logs, and sensors.Silver Layer:
The Silver layer is the second layer of the Medallion Architecture. This layer is responsible for cleansing, transforming, and integrating the data stored in the Bronze layer. The goal of this layer is to ensure that the data is accurate, consistent, and relevant.The Silver layer is where data quality checks are performed, and any missing or incorrect data is corrected. Data is transformed and merged to create a unified view of the organization's data. The data in this layer is also optimized for querying and reporting.
For example, using the same e-commerce website, the Silver layer of the data warehouse would integrate the transaction data with data from other sources, like customer demographic data or product inventory data. The Silver layer would also ensure that all the data is accurate, consistent, and ready for analysis.
Gold Layer:
The Gold layer is the final layer of the Medallion Architecture. This layer is responsible for providing a business-friendly view of the data stored in the Silver layer. The goal of this layer is to enable business users to easily access and analyze the data.The Gold layer contains pre-calculated metrics, aggregates, and summaries that are optimized for analysis and reporting. This layer also includes data models and hierarchies that are specifically designed for the needs of the organization.
For example, using the same e-commerce website, the Gold layer of the data warehouse would contain pre-calculated metrics like total revenue, average order value, and conversion rate. These metrics would be optimized for reporting and analysis, making it easy for business users to track the performance of the website and make informed decisions.
Conclusion: The Medallion Architecture is a popular approach for designing data warehouses that can effectively meet the needs of an organization. The Bronze, Silver, and Gold layers provide a framework for storing, integrating, and analyzing data in a way that is accurate, consistent, and business-friendly. By following this approach, organizations can create a robust data warehouse that can drive informed decision-making and improve overall performance.
Comments
Post a Comment